Workflow diagram: Visualize and optimize your processes
Tempo Team
Understanding the process is often the hardest part of getting work done.
You know the goal. You have the right team. But somewhere between task assignments, handoffs, and approvals, things get complicated. Miscommunication happens, and no one’s sure who’s responsible for what – or when.
A workflow diagram eliminates uncertainty by visually mapping out the steps and stakeholders involved in each task. It provides a clear, structured overview that aligns teams, reduces confusion, and improves collaboration.
With a well-designed workflow diagram, even the most complex projects are easier to manage and execute.
Here, we’ll explore the types of workflow diagrams and show you how to create one.
What is a workflow diagram?
A workflow diagram is a visual tool that outlines the sequence of tasks, decisions, and responsibilities required to complete a process. Whether you’re onboarding a new hire, handling a client request, or managing a complex software development cycle, this diagram provides a blueprint of how work moves from start to finish.
Workflow diagrams typically use shapes – such as rectangles for tasks and ovals for start or end points – connected by arrows to represent the flow of work. These visual elements, known as flowchart symbols, make complex workflow processes easier to understand and follow.
Types of workflow diagrams
There's no one-size-fits-all approach when mapping a process. Different types of workflow diagrams serve distinct purposes, whether you’re managing a simple task flow or coordinating a complex, cross-functional project. Understanding the most common workflow diagram examples helps you choose the right one for your team.
Here are four types of workflow diagrams that allow you to visualize processes and keep work running smoothly:
ANSI flowchart
An American National Standards Institute (ANSI) flowchart uses standard flowchart symbols (e.g., rectangles for tasks, diamonds for decisions, and ovals for start or end points) to represent the steps in a process.
Use case: An ANSI flowchart suits straightforward, step-by-step tasks or smaller projects where clarity and simplicity are key. It’s especially helpful when you need to clearly outline a process without getting bogged down in unnecessary detail.
UML activity diagram
A UML activity diagram, part of the Unified Modeling Language, is designed to map out a system's control flow – the sequence in which actions or activities are executed based on conditions and events. It offers more detail than an ANSI flowchart by showing how tasks are coordinated and the conditions that trigger each step. Common elements include arrows, decision nodes, and swimlanes, which clarify responsibilities across different roles or departments.
Use case: Create a UML activity diagram when working with complex systems or workflows that involve multiple interdependent tasks. It’s useful for software development or projects that require detailed coordination across various components.
BPMN diagram
A Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) diagram is an advanced workflow diagram used to document and analyze business processes. It uses standardized symbols and notation to represent tasks, events, decision points, and data, making complex workflows easier to understand and communicate. BPMN helps teams identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement within a process.
Use case: Build a BPMN diagram when you’re managing complex business processes and want to analyze performance or streamline operations. It’s ideal for modeling workflows that span multiple teams or departments, particularly when you need to pinpoint delays or bottlenecks.
Swimlane diagram
A swimlane diagram organizes a workflow into horizontal or vertical lanes, with each lane representing a person, team, department, or role involved in the process. This format helps visualize responsibilities, track task ownership, and show how work moves between stakeholders.
Use case: Develop a swimlane diagram for processes that involve multiple teams or individuals. It’s particularly useful for managing project workflows or any scenario where you must define roles, responsibilities, and task handoffs.
How to create a workflow diagram
A workflow diagram can transform the way you approach and manage processes. Consider building one when you face an unclear process or need to improve collaboration across teams. Follow this step-by-step guide to build an effective workflow diagram:
1. Select the right diagram type
Choose the workflow diagram type that best suits your needs. Are you outlining a straightforward process with clear steps, or do you need to represent a complex system with multiple stakeholders? If you're unsure, start with a flowchart or swimlane diagram.
2. Identify the steps and stakeholders
Identify the crucial steps in the process to create an accurate workflow diagram. Each step should represent a specific task or action that moves the process forward.
Next, determine who’s responsible for each step. These stakeholders may be team members, departments, or external partners. Identifying these roles ensures clarity and accountability within the workflow diagram.
For instance, in a swimlane diagram, you’ll assign each lane to a specific stakeholder or department to show who’s responsible for each task.
3. Collect necessary information
Gather all the information needed to build a complete workflow diagram, including:
A detailed description of each step in the process
Inputs and outputs for each task (e.g., what triggers the next step, what you produce, etc.)
Essential tools or systems for each task
Any rules or conditions that affect the process flow (e.g., approvals or decision points)
This information provides the foundation for your workflow diagram, ensuring it accurately reflects processes.
4. Map out the steps visually
Create your workflow diagram using tools such as Lucidchart, Microsoft Visio, or Google Drawings. Many of these tools offer workflow diagram templates that save time and help structure the diagram.
Start by representing each task with a shape. Rectangles typically signify tasks or actions, whereas diamonds indicate decision points where the workflow branches based on conditions. Use arrows to show the direction of the process flow. If the workflow involves loops or repeated steps, clearly illustrate them to highlight the process’s iterative nature.
Consider how you organize the steps. Are the tasks happening in parallel or sequentially? Do certain steps require approval or sign-off from stakeholders before they proceed? Clarify these details in the workflow diagram.
5. Design your workflow
Finally, design and refine your workflow diagram for clarity and usability. Here are a few guidelines to help you create an effective visual:
Use consistent shapes and symbols: Whether you're using a flowchart template or starting from scratch, use the same shapes for similar tasks to maintain visual consistency.
Make it easy to read: Avoid clutter by spacing out elements and using clear, concise labels for each step and decision point. Keep it simple so anyone can understand the diagram at a glance.
Incorporate color coding: Use colors to differentiate between categories, such as departments or task types (e.g., blue for administrative tasks, green for development tasks). This visual cue helps users quickly interpret the diagram.
Add annotations or notes: Include brief annotations or notes if a step or decision point needs further explanation. This enhances clarity, especially for team members unfamiliar with every part of the process.
6. Review and refine with stakeholders
After designing your workflow diagram, review it with relevant team members or stakeholders. Feedback from those involved in the process can identify gaps, clarify ambiguous steps, and confirm the diagram accurately reflects how the work flows in practice. This collaborative review strengthens the final diagram and fosters alignment and accountability across the team.
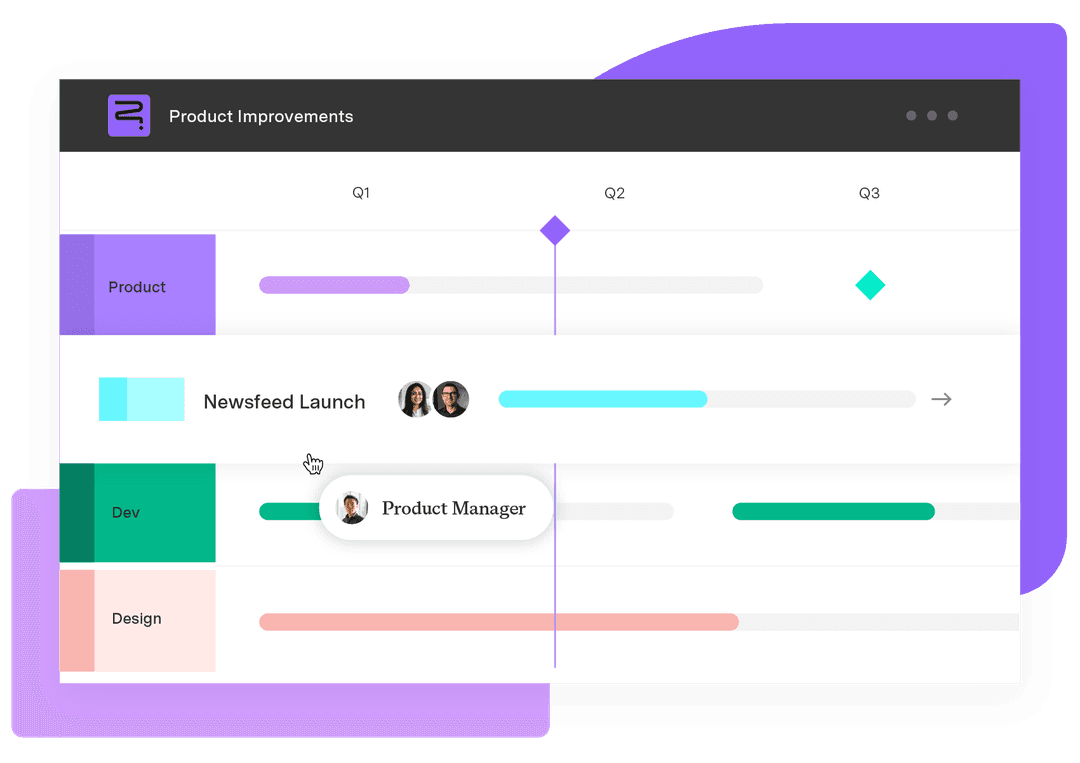
Connecting workflow visualization to execution with Tempo
Once you’ve created your workflow diagram, the real value comes from turning it into action. Tempo’s project management tools help you transform static visuals into dynamic, real-time processes – all within Jira.
With Strategic Roadmaps, you can visualize timelines, dependencies, and progress across teams to keep everyone aligned. Custom Charts for Jira offers clear visibility into resource use and shifting priorities so you can make informed decisions faster.
Tempo also supports SAFe flow reporting in Jira, allowing you to monitor how work moves through each stage and spot process inefficiencies early. For deeper insights, leverage Jira’s software reporting with Custom Charts to track the performance metrics that matter most to your team. And with Tempo’s intelligent forecasting tools, you can confidently predict project completion dates and deliver on time.
Ready to bridge the gap between planning and execution? Try Tempo today to optimize your workflows and achieve meaningful results.